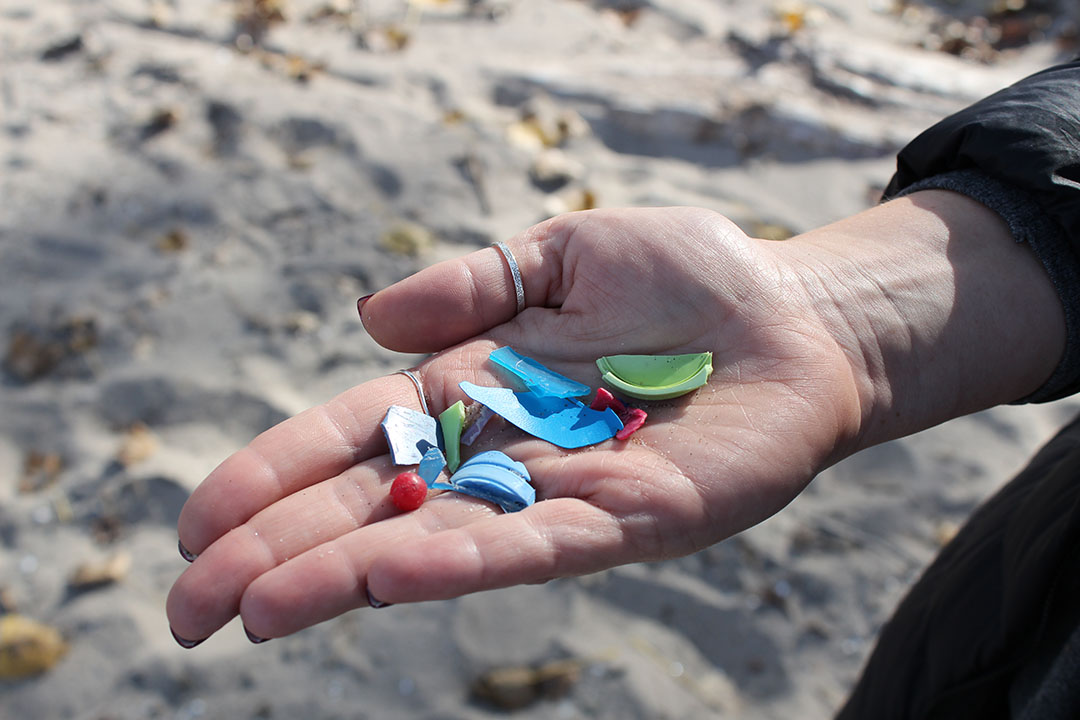
A day at the beach doesn’t often involve lab work, but for a group of Brock University fourth-year Geography students tasked with assessing plastic waste on the shores of Lake Ontario last fall, it was just that.
Back in October, students from Professor of Geography and Tourism Studies Michael Pisaric’s GEOG 4P26 class visited Sunset Beach in north St. Catharines to measure the quantity of plastics turning up in the sand.
Students measured out plots on the beach and sifted through the sand to collect as many tiny pieces of plastic as they could. They compiled their findings in lab reports for the end of the Fall Term.
The results are now in, and they’re alarming.
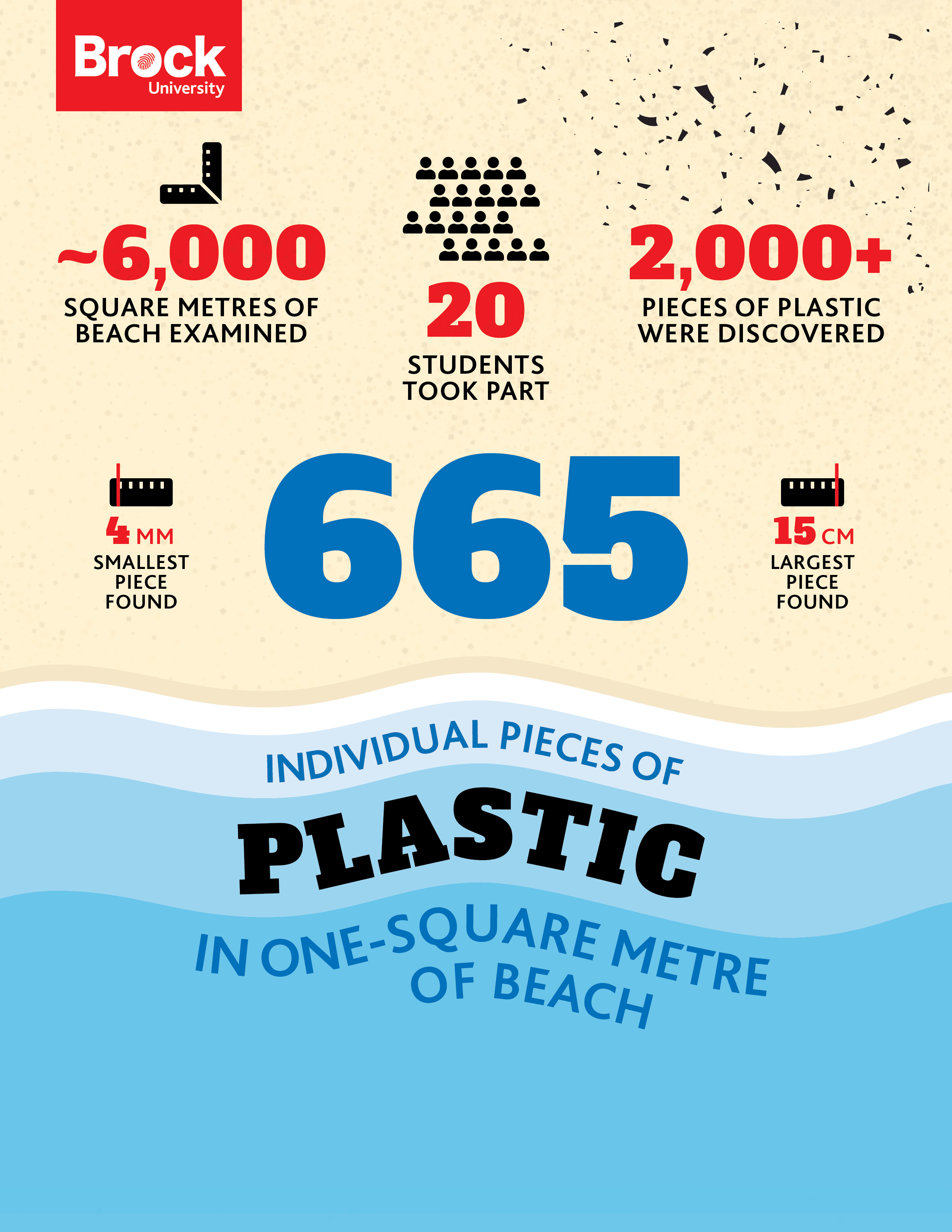 In one sample alone, one square metre of the beach yielded 665 individual pieces of plastic material.
In one sample alone, one square metre of the beach yielded 665 individual pieces of plastic material.
Pisaric called the amount and variety of plastics collected in the samples “striking.”
“I think much of the discussion concerning plastics in the environment has been focused on the oceans and we are quickly understanding that plastic pollution is also an important issue closer to home in the Great Lakes,” said Pisaric, who is also Chair of the Geography and Tourism Studies Department. “This small study of a single beach on Lake Ontario clearly shows the prevalence of plastic pollution in our own backyard is a serious problem.”
Emily Bowyer, a third-year student from Mississauga majoring in Geography and Biology who participated in the field collection, described it as “an opportunity to see the magnitude of the problems in the environment first-hand.”
Another surprise to the team was the prevalence of nurdles — small plastic pellets used in the manufacture of many different goods.
Investigation during the course uncovered a 2013 Toronto Star article that suggested nurdles may have made their way into Lake Ontario via the Humber River during a factory fire.
“It is interesting to speculate that the prevalence of nurdles we noted in our samples may have originated on the other side of Lake Ontario,” Pisaric said.
The professor plans to run a similar investigation when the course is offered again next fall to address some of the questions that cropped up in light of the results of the students’ labs.
“Perhaps next time around I will have the students compare the beaches on Lake Ontario with a beach on Lake Erie,” he said. “Are similar quantities of plastics occurring in both areas? Do the types of plastic differ between the two lake environments?”
Carolyn Finlayson, Experiential Education Co-ordinator for the Faculty of Social Sciences, attended the field trip and witnessed how interested casual beach visitors were in the students’ activities.
“It’s a wonderful example of the larger impact experiential learning can have on our Niagara community and our students,” she said. “By working at the beach that day for their lab, students were able to start conversations with beachgoers about their use of plastic and its impact on the shorelines they enjoy.”
Cara Krezek, Director of Co-op, Career and Experiential Education, said these were exactly the types of courses the University envisioned when it committed to expanding experiential learning so all students had access to meaningful experiences in their programs.
“Courses like these take our students into a real-world setting and allow them to apply their knowledge, learn new skills and reflect on how they can take these experiences forward to a future career path,” Krezek said. “I am certain these students will never forget their findings and it will change the way they interact with plastics.”
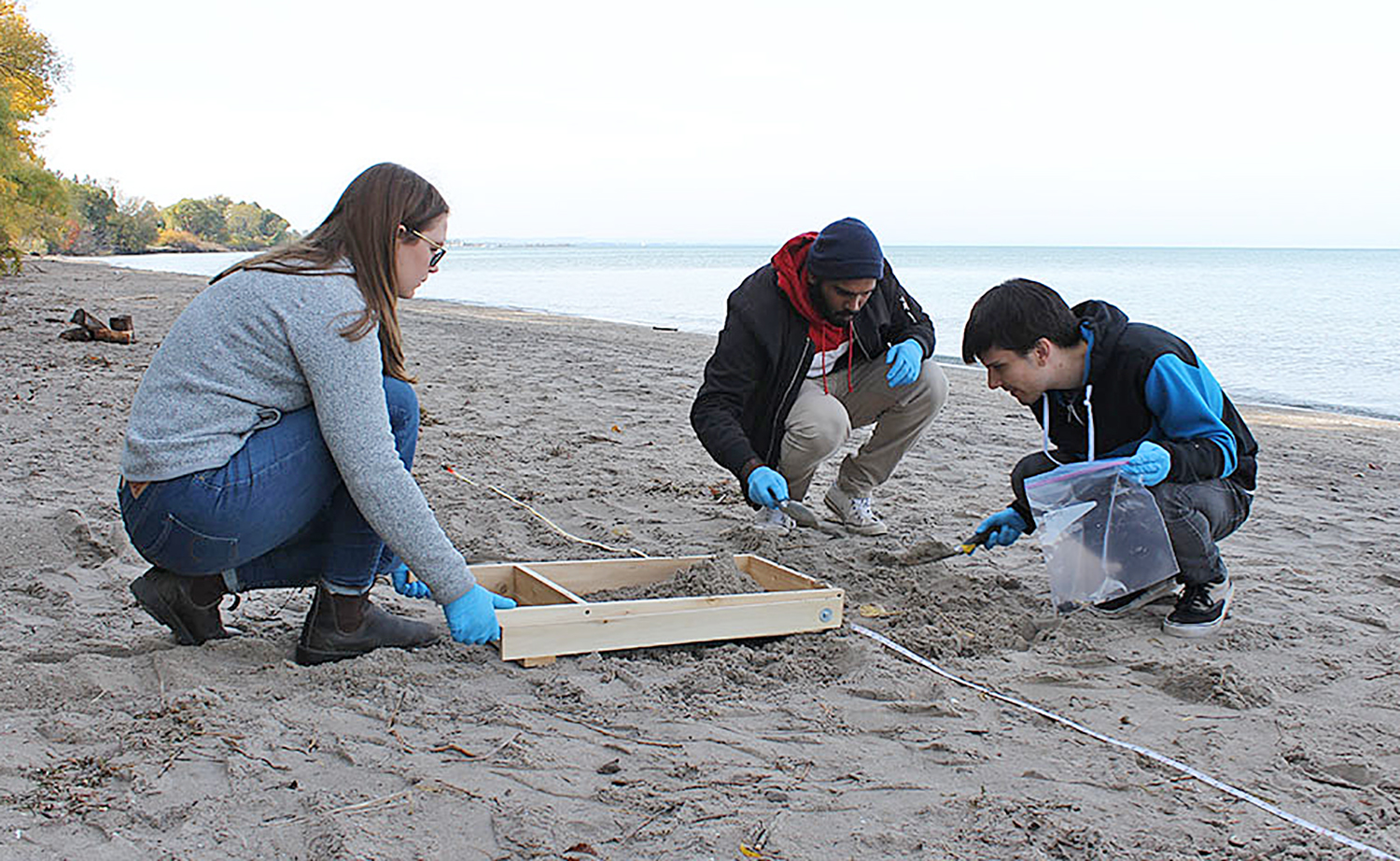

Emily Bowyer, Pravin Rajayagam and Dakota Schnierle, students in a fourth-year Geography course at Brock, sift through sand on Sunset Beach in St. Catharines to find out how many plastics are washing up on the beach.
STORY FROM THE BROCK NEWS
Other Media Coverage
Brock students find alarming amounts of plastic at St. Catharines beach: Extensive media coverage was given to an experiential learning exercise led by Professor of Geography and Tourism Studies Michael Pisaric that saw Brock students uncover more than 2,000 pieces of plastic on St. Catharines’ Sunset Beach. The story was featured in the St. Catharines Standard, CBC, CHCH, Newstalk 610 CKTB and Coastal News Today.









