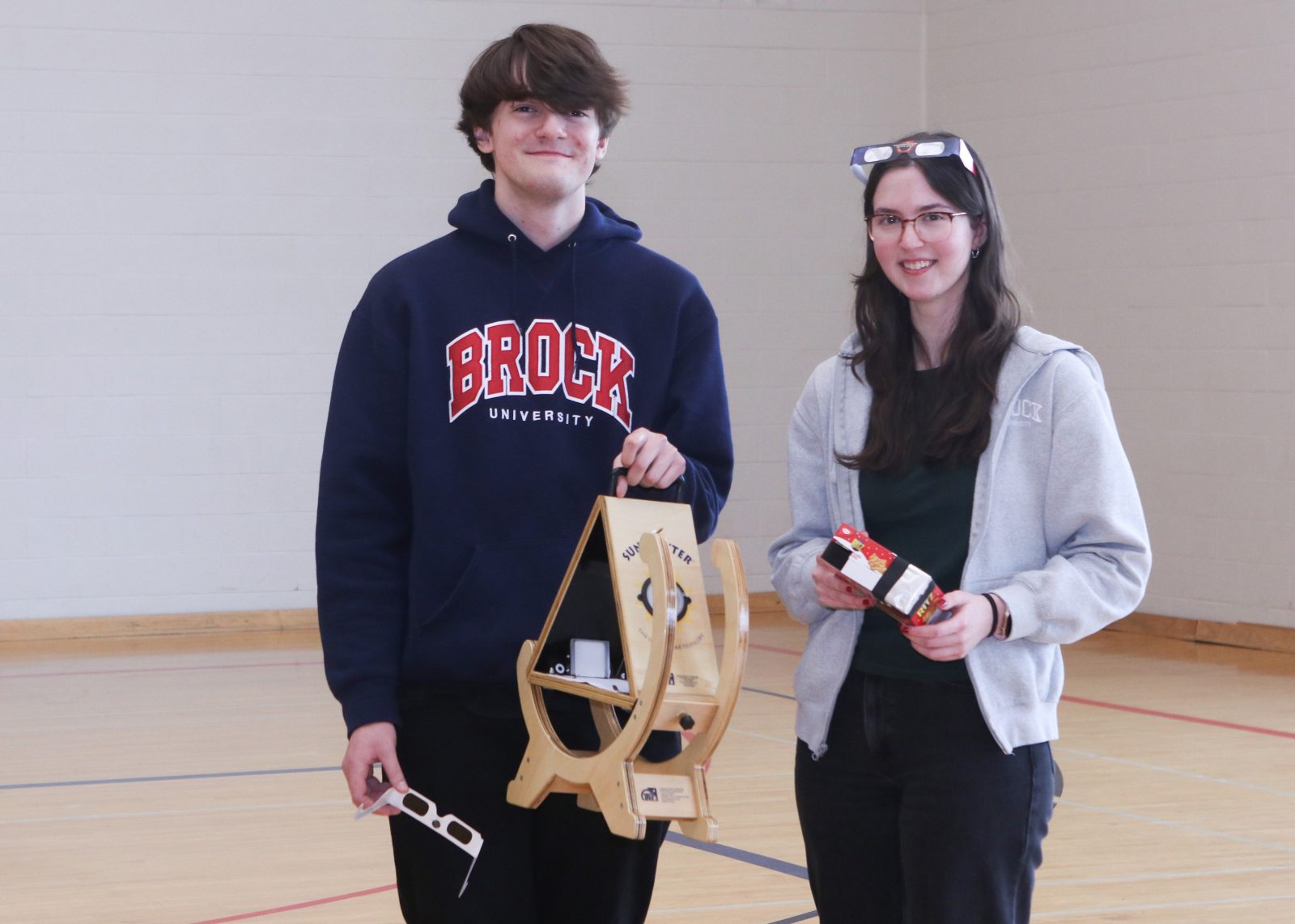
Second-year Concurrent Teacher Education students Justus McRae and Sophie Della Manna hold a Sun Spotter and a pinhole camera, which are devices that can be used to safely view the solar eclipse. Brock’s Eclipse on the Escarpment event on Monday, April 8 will feature several educational exhibits, including a live demonstration on how to make a pinhole camera.
As Niagara prepares to witness the rare total solar eclipse, Brock University is welcoming the community to campus Monday, April 8 for a learning experience like no other.
Eclipse on the Escarpment will feature more than a dozen free educational exhibits that will engage adults and children alike in science, history and culture through interactive experiments, hands-on projects, informative posters and interesting simulations, followed by a community viewing of the total solar eclipse.
Among the experiences, which begin at noon in Ian Beddis Gymnasium, will be a live experiment that will see Biology researchers use an infrared thermal imaging camera to monitor the reaction of Oxalis plants during the darkness of the total solar eclipse.
“Oxalis are known to display rapid plant movement by retracting their leaves towards the shoot when kept in darkness. This phenomenon seems to be mediated by a protein called phototropin,” says Alonso Zavafer, Assistant Professor of Biological Sciences and Engineering. “Phototropin acts as a light switch by detecting blue light and controlling the internal water level of the leaves. During the day, there is blue light and the leaves open, while at night when only far-red and near infrared light is present, the leaves close.”
Zavafer says the reaction is believed to be an evolutionary response to promote photosynthetic growth during the day and prevent dehydration of the leaves at night. He expects the plants will close their leaves during the total solar eclipse when the sun is blocked by the moon.
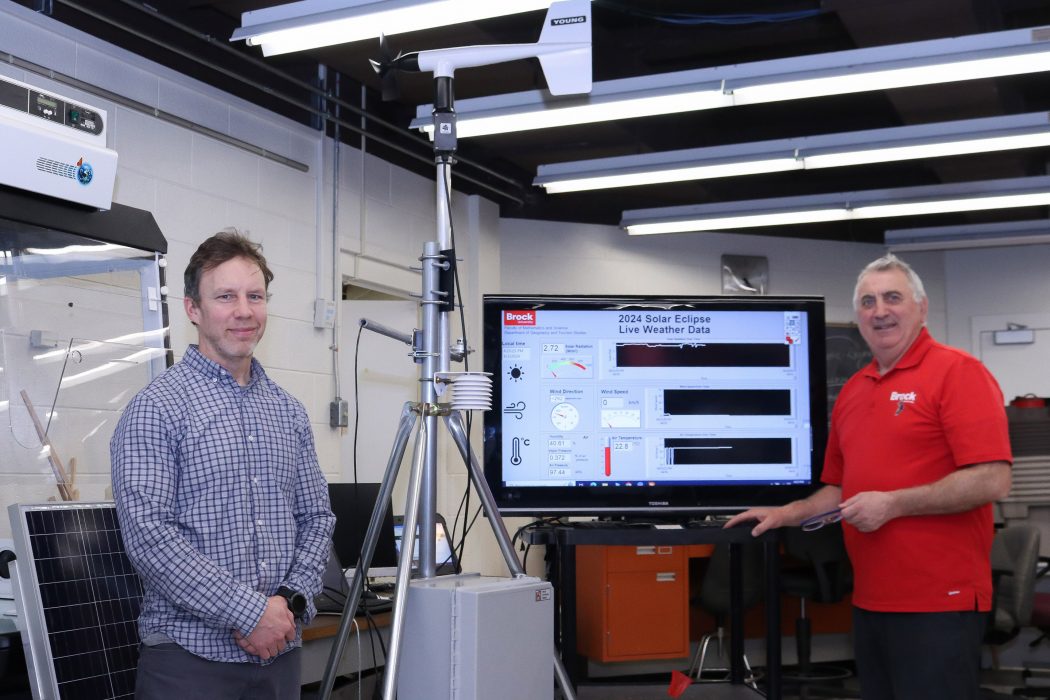

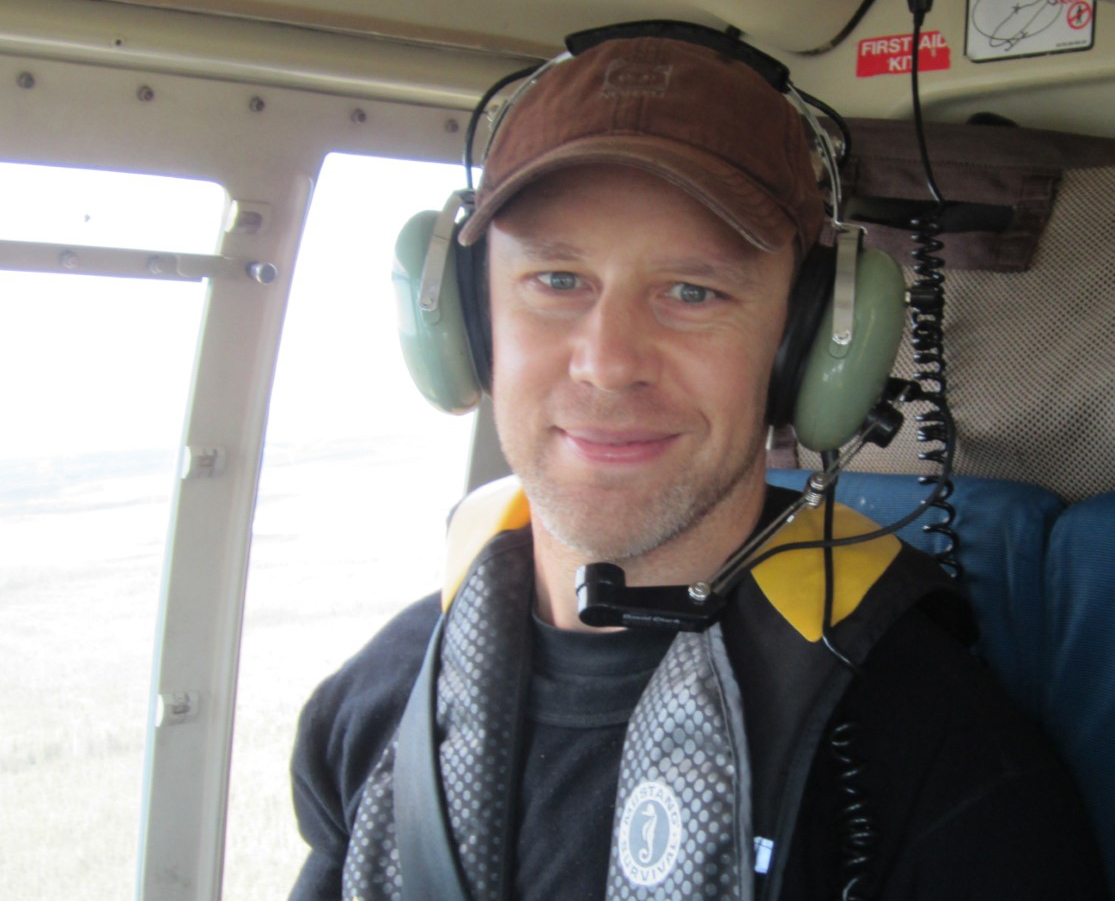
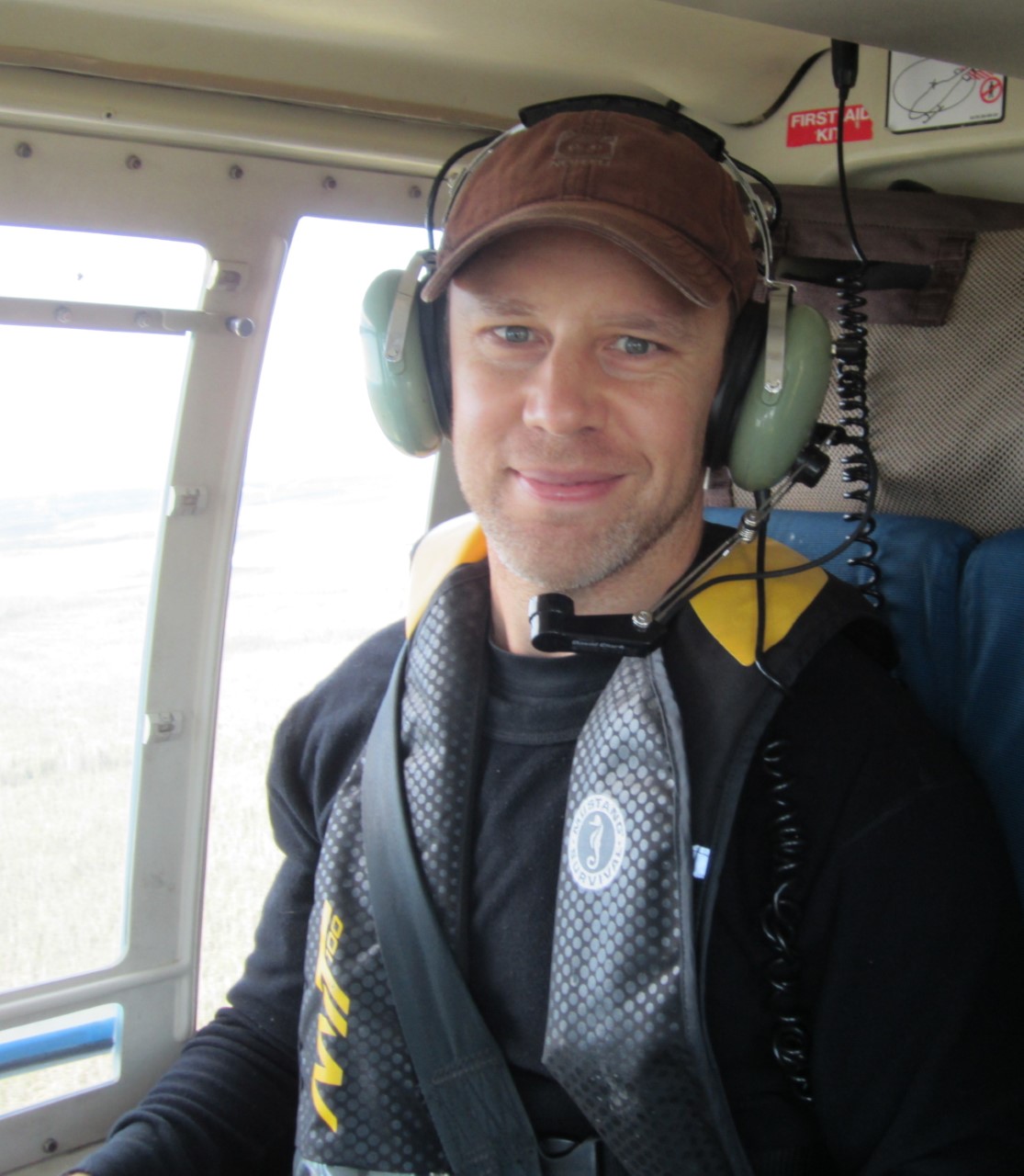
Kevin Turner (left), Associate Professor of Earth Sciences and Geography and Tourism Studies, and Dimitre Iankoulov, Micro Support Analyst/Technician with the Department of Geography and Tourism Studies, have been testing the scientific weather station they will use to measure and record shortwave radiation, temperature, humidity and wind speed and direction during the solar eclipse on Monday, April 8.
“Plants can move and sense the day and night cycles,” he says. “Our experiment will show plants can be fooled by the eclipse into thinking they are experiencing a night cycle.”
Other exhibits will explore animal behaviour during an eclipse, the role of the 1919 eclipse in confirming the theory of general relativity, the 17th-century poem titled “The Eclipse,” ancient tools used to calculate and display celestial information. the history of the moon, and a NASA initiative involving a computer simulation of a lunar rover that follows the physics of the moon.
A chemistry-focused exhibit will highlight the celestial origins of the elements in the periodic table with physical examples participants can touch, while an exhibit led by Earth Sciences faculty and students will feature a display of meteorite and rock samples, a moon photo selfie station and a hands-on demonstration on creating an impact crater.
Physics students will demonstrate how to create a pinhole camera, which can be used to safely view the eclipse as a projection on paper. Visitors can bring a cereal box or similarly sized cardboard container to make their own.
Guests from Niagara College solar spectroscopy, Niagara Geopark, SETI Institute and Space Place Canada will also be on site, many using specialized equipment to view, monitor or livestream the eclipse.
Among the scientific observations expected to take place on campus will be the use of a digital smart telescope to observe physical, meteorological and biological phenomena, while also livestreaming the eclipse to the Brock University YouTube channel with the assistance of BrockTV.
Brock’s Department of Geography and Tourism Studies will be using a scientific weather station during the eclipse to measure and record changes in temperature, humidity, wind speed and direction, as well as shortwave radiation, which is the sun’s energy reaching the Earth each second.
The community viewing will take place on Alumni Field from 2 to 4:30 p.m., with the eclipse reaching maximum totality at 3:19 p.m.
Solar eclipses can be safely viewed with the use of ISO-certified eclipse glasses. Looking directly at the sun with the naked eye can cause permanent eye damage. Complimentary viewing glasses will be available on Monday, April 8 in Ian Beddis Gymnasium from noon to 3 p.m. or at several locations across campus beginning at 11 a.m. on a first-come, first-served basis, while quantities last.
People coming to campus for the event are reminded that paid parking is available through the Honk mobile app. Parking may also be paid in person at a kiosk inside the Walker Sports Complex near the Hungry Badger from 9 a.m. to 4 p.m.
Visitors travelling to campus are encouraged to arrive early to avoid traffic delays and to consider taking public transportation.
Those looking to enhance their eclipse experience are invited to attend one of two free public lectures this week about the celestial spectacle and the significance of lunar and solar cycles.
Brock representatives will also be out in the community this weekend. Physics students and professors will be at the Niagara Parks Power Station from Friday, April 5 to Sunday, April 7 showcasing eclipse-viewing tools such as a telescope and Sun Spotter, and leading children in a sun colour-changing activity.
Brock’s Let’s Talk Science team will be leading eclipse-related hands-on activities Monday, April 8 from 10 a.m. to 4 p.m. at the Vale Health and Wellness Centre in Port Colborne as part of the City of Port Colborne’s eclipse programming. Activities include creating a pinhole camera and eclipse art.
For more information about Eclipse on the Escarpment, please visit brocku.ca/eclipse
Story reposted from The Brock News