
ABI Information
What is an Acquired Brain Injury?
An acquired brain injury (ABI) is any type of sudden injury that causes temporary or permanent damage to the brain. This damage is associated with some kind of trauma to the head such as concussion, a fall, or a motor vehicle accident (traumatic brain injury). Injuries can also occur as a result of anoxia (e.g. near drowning), toxicity, infection, or cerebral vascular accident (CVA, e.g., stroke): falls (28%), MVC (20%) and other factors (7%) such as abuse, disease, anoxia, or drowning (Langlois, 2005)
ABIs account for 30% of all paediatric injuries; and is the leading cause of death and disability in children and adolescents (U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, 1999).
Challenges in the Classroom
Educators need to remember that students with ABI can have complicated medical and health needs. A student's brain is a developing organ and as a result occasionally as the student gets older, new symptoms can appear even years after the brain injury. Other students may have chronic pain from the injuries they incurred, abd therefore may not be able to maintain positive behavioural functioning. Headaches are a common effect of the injury and can lead to disruptions in attention and concentration, then leading to frustration and agitation.
Young students with ABI may have injured part of the brain whose associated function will mature later in development. These students may appear to have returned to normal soon after injury, however later they experience substantial difficulty because the brain interferes with the development of the function that needs to mature.
Epidemiology of TBI
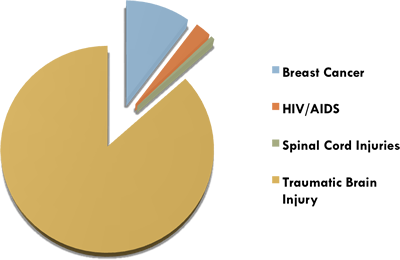 |
|
| Paediatric TBI accounts for 1.5/1000 emergency department visits per annum (Canadian Institute for Health Information, 2006). | |
Implications for Youth
- the cognitive, emotional, social, and physical challenges experienced by these children and youth do not resolve quickly
- can continue for many years or even for the duration of his/her life – well beyond discharge back to his/her community (e.g. Donders & Strom, 2000; Rumney, 2007)
- children who have sustained moderate to severe TBI report significantly lower health-related quality of life, in particular in the domain of psychosocial functioning relating to school, relative to other heterogeneous sample of chronically ill children (Erickson, Montague & Gerstle, 2010)
Please contact us for further information.
(905) 688-5550 ext. 3556 or ext. 5523
© 2012 Brock University

